|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Talks & Events
|
Ph.D. Thesis Defenses: 2018
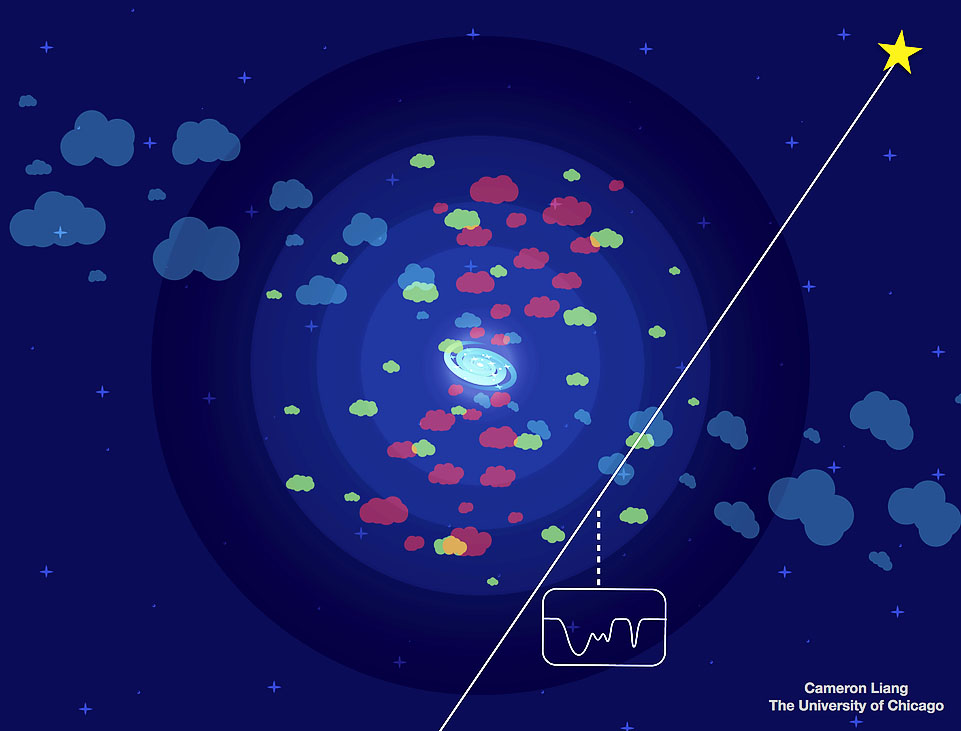
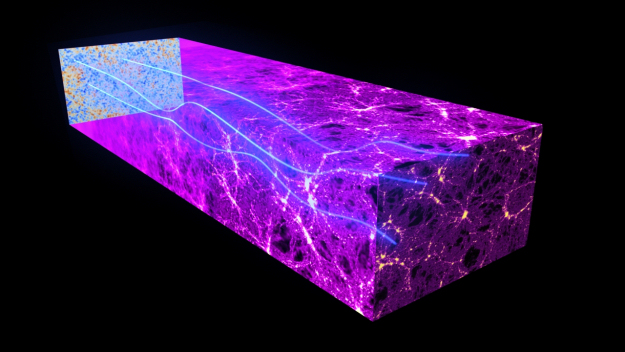
Sunyaev Zel'dovich Effect Observations of X-ray Cavities in Galaxy Clusters "Zubair has done it all, from building 10 ultra-sensitive receivers, commissioning them on CARMA, developing the data reduction pipeline, to imaging and analyzing the first Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect imaging of x-ray cavities in galaxy clusters. His thesis places tight constraints on the nature of plasma within the cavities and mechanisms for heating of the inter cluster medium." - John Carlstrom, Ph.D. advisor Multiphase Gaseous Halos around Galaxies There is no doubt that our atmosphere is an integral part of the ecosystem of the Earth. Everyday weather and long-term climate of the atmosphere are directly linked to activities on the surface of the Earth and vice versa. Gaseous halos, known as the circumgalactic medium (CGM), are the equivalent atmospheres of galaxies. In this thesis, I provide a major step towards the empirical constraints and theoretical modeling of the CGM and the co-evolution with their host galaxies. Using background quasars, I statistically map the spatial extent of multiphase gaseous halos in a sample of ~200 galaxies that span nearly five orders of magnitude in stellar mass, from dwarf to L*, and more massive galaxies. With these empirical constraints, I explore the effects of theoretical modeling of star formation and feedback processes using a set of high-resolution cosmological zoom-in simulations of a Milk-Way progenitor. To connect more closely with observations, I develop a synthetic absorption pipeline, as a virtual telescope, to observe the simulated galaxy and their CGM. This series of observational and theoretical studies have led to new insights of the cold gas in galactic winds and halos. I explore a new model, the circumgalactic mist, with a set of magneto-hydrodynamic simulations. I will present the model implications on the spatial distribution of multiphase gas around galaxies. The Propagation of Flame Fronts Through Inhomogeneously Magnetized Plasma Ph.D. Committee members: Fausto Cattaneo (PhD advisor), Doyal "Al" Harper, Arieh Konigl, and Robert Rosner. Thesis Abstract: The effects of an inhomogeneous magnetic medium on the propagation of magneto-hydrodynamical (MHD) laminar flame fronts are investigated. This investigation is motivated by the occurrence of magnetized thermonuclear combustion in several astrophysical systems. Magnetized thermonuclear burning occurs on the surfaces of neutron stars during Type I X-ray bursts, within the interiors of white dwarfs during Type Ia supernovae, during classical novae, and may be important for certain core collapse supernovae as well. Thermonuclear flames that propagate in these systems travel through inhomogeneous magnetic fields. We present the results of a series of numerical simulations of magnetized flame propagation conducted using the MHD extension to the High-Speed Combustion and Detonation (HSCD) code. A simplified flame model is used with one-step Arrhenius kinetics, a perfect gas equation of state, and constant thermal conductivity coefficients. Although idealized, the model allows for the opportunity to study the physics of the problem without the complexities of the nuclear kinetics of thermonuclear burning. We simulate the propagation of laminar flames through inhomogeneous magnetic media. A changing magnetic medium significantly alters the structure of the flame through the generation of an electric current that propagates out of the plane of the flame front. The electric current rotates the direction of the magnetic field across the flame and produces strong shear flows. Furthermore, for flames that conduct heat anisotropically and that propagate at an angle to the magnetic field, the flame speed increases due to the non-uniform magnetic field. Naturally occurring flames in astrophysical systems may experience similar changes to their structure and speed that would influence the observational properties of these systems. Effects of Redshift Uncertainty on Cross-Correlations of CMB Lensing and Galaxy Surveys Ph.D. Committee members: Josh Frieman (PhD advisor), Scott Dodelson, Steve Kent, Dan Hooper Thesis Abstract: Wide-field galaxy imaging surveys, such as the Dark Energy Survey (DES), and cosmic microwave background experiments, such as the South Pole Telescope (SPT), have great synergy in studying the large-scale structure of the Universe. One of the most important combined measurements from these types of surveys is the cross-correlation of galaxy positions with locations of gravitational lensing of the CMB. In this thesis, I go in depth in projecting future cosmological constraints of this measurement. The key element of my work that has not been studied previously is the effect of redshift uncertainties on these constraints. I will show that discounting this effect can greatly overestimate the precision of these measurements. I will also show how some of this loss of precision can be mitigated, going from 50 times larger uncertainties than the perfectly known redshifts case, to only 2-3 times larger. A secondary goal of my work is to show that these measurements can simultaneously constrain the redshift information of samples of galaxies. I will show that these constraints on redshift information can be competitive with typical methods of estimating photometric redshifts. I will discuss projections of both the current DES/SPT era, and the exciting future era (2020s) of the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) and the CMB-Stage 4 experiment. |